Health and safety at work are not just legal obligations for employers but essential components in ensuring a productive, safe, and supportive environment for everyone. Employees play a key role in maintaining a safe workplace, and knowing your rights, responsibilities, and the best practices for safety is crucial. Whether you work in an office, a warehouse, or on construction sites, understanding health and safety measures can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, injuries, and health problems. Here’s what every employee needs to know.

1. Know Your Rights and Responsibilities
Health and safety laws are in place to protect workers, and as an employee, you have the right to a safe and healthy workplace. Your employer is required by law to:
- Identify and assess risks
- Implement appropriate safety measures
- Provide training and personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Ensure safe working conditions
In turn, employees have a responsibility to:
- Follow health and safety instructions
- Use equipment and protective gear as required
- Report unsafe conditions or practices
- Take care of their own health and safety, as well as that of others

Courses like the Level 1 Award in Health and Safety at Work (RQF) provide foundational knowledge about health and safety practices, giving employees a solid understanding of their role in maintaining a safe work environment.
2. Common Workplace Hazards
Different workplaces have different types of hazards, but common risks include:
Slips, trips, and falls: Often caused by wet floors, poor lighting, or obstructions in walkways.
- Manual handling injuries: Lifting, carrying, or moving objects improperly can cause musculoskeletal injuries.
- Chemical exposure: In environments where chemicals are used, improper handling or lack of PPE can lead to respiratory issues or skin damage.
- Noise: Long-term exposure to loud environments can lead to hearing loss.
- Stress and mental health: Workplace pressures and poor work-life balance can result in burnout or other mental health issues.

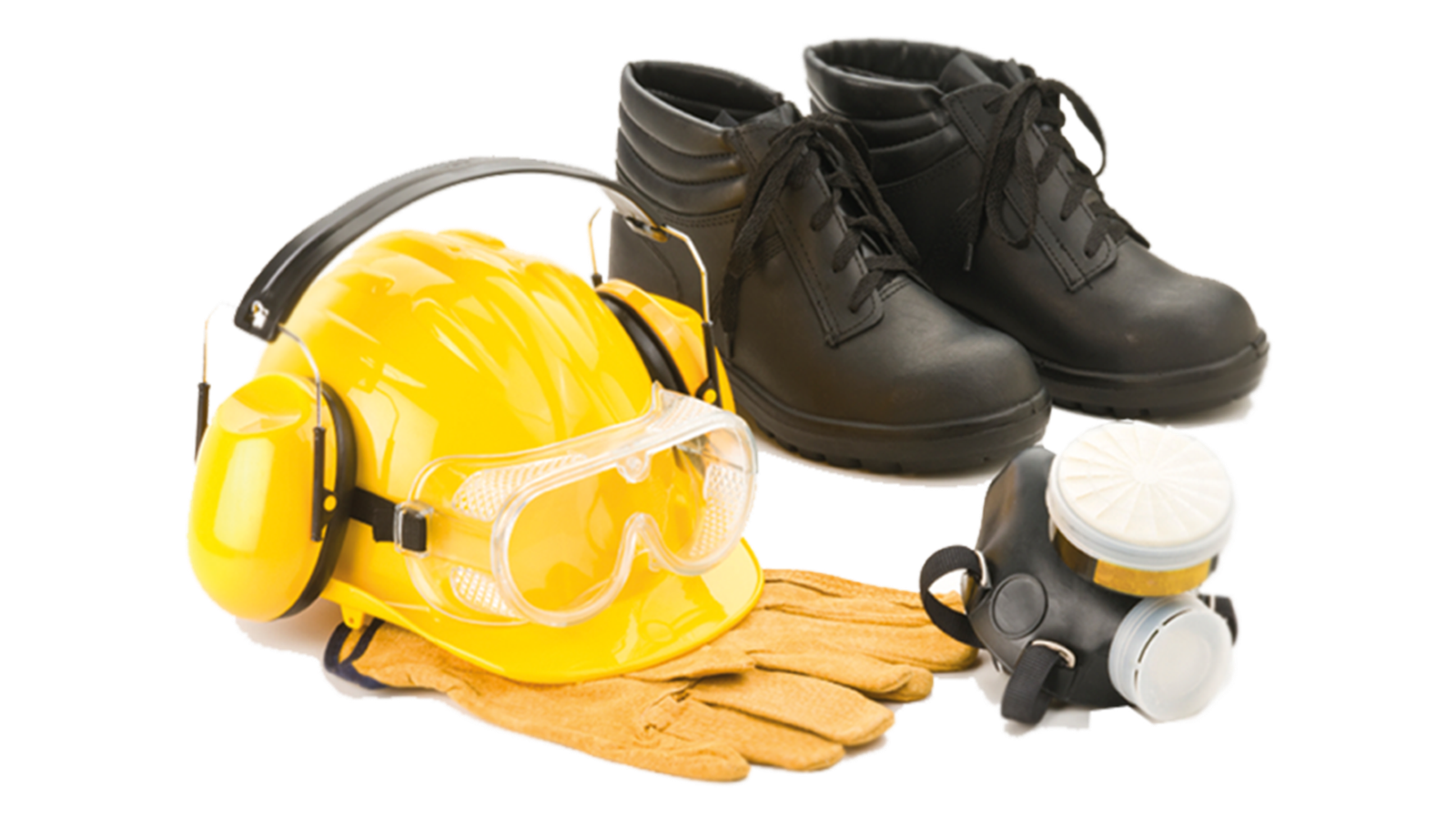
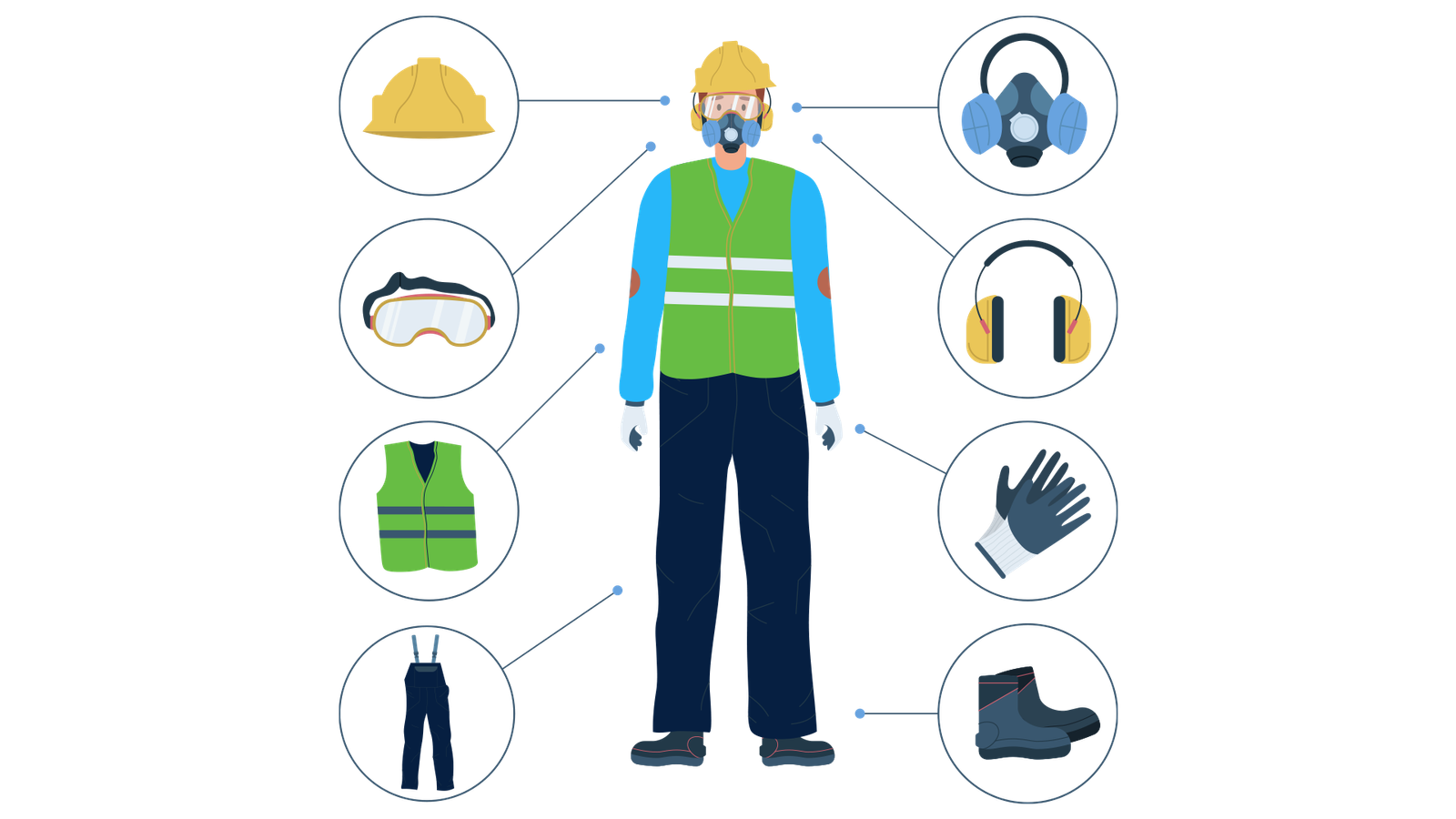
3. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
In certain jobs, using PPE is essential to reduce the risk of injury or illness. PPE may include gloves, helmets, goggles, high-visibility vests, or respiratory equipment. It’s important to:
- Wear the right PPE for the job
- Ensure PPE is properly maintained and clean
- Replace worn-out or damaged equipment
- Report any issues with PPE to your employer
4. Emergency Procedures
Every workplace should have clear procedures for dealing with emergencies, such as fires, electrical failures, medical emergencies, or chemical spills. As an employee, you need to:
- Be familiar with fire evacuation routes and assembly points
- Understand how to report incidents or accidents
- Be aware of first-aid stations and trained personnel
Add Your Heading Text Here
5. Training and Education
Employers should provide training on health and safety practices specific to your workplace. This may include:
- Fire safety drills
- First-aid training
- Ergonomics in the workplace
- Safe use of machinery or hazardous substances
As an employee, it’s essential to engage in training and always ask questions if you’re unsure about any safety protocols. Regular refresher courses, such as the Level 2 Award in Health & Safety in the Workplace (RQF), may also be necessary to keep safety practices top of mind.
6. Reporting Accidents and Hazards
It’s important to report any accidents, near-misses, or hazards you encounter. Even if an incident doesn’t result in injury, reporting it can prevent more serious accidents in the future. Every workplace should have a system in place for employees to report unsafe conditions or incidents.

7. Mental Health and Well-being
Health and safety at work aren’t just about physical safety; mental health is equally important. Long hours, excessive workload, and lack of support can lead to mental health issues such as stress, anxiety, or depression. Employers should provide a supportive environment that includes:
- Regular breaks
- Stress management resources
- Employee assistance programs (EAPs)
- A clear policy on mental health

8. Staying Informed
Health and safety guidelines may change over time, especially with new technology, regulations, or processes. Stay informed by:
- Attending regular health and safety meetings
- Reviewing safety procedures as they are updated
- Asking your employer for clarification when necessary

Conclusion:
Health and safety at work is a shared responsibility that requires cooperation between employers and employees. By understanding your rights and responsibilities, staying informed about workplace hazards, and actively participating in safety practices, you can contribute to creating a safe and healthy working environment for everyone.
Safety is not just about avoiding accidents—it’s about fostering a culture of care, respect, and well-being in the workplace. Always prioritize safety, and don’t hesitate to speak up if you notice potential risks or hazards. After all, your health and safety are worth protecting.



